Manage and streamline operations across multiple locations, sales channels, and employees to has improve efficiency and your bottom line.
- Pune
- 7719917444
- rajendra@puneinvest.com
- https://puneinvest.com
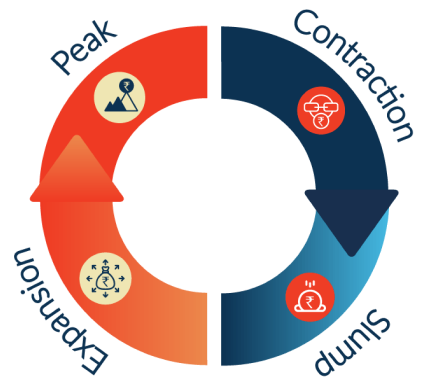
The Business Cycle explained
Every economy, regardless of location, typically experiences four distinct phases of the business cycle:
This phase, known as the recovery phase, follows an economic downturn. During this period, economic activity begins to rebound, with GDP expanding, unemployment declining, and consumer spending rising. As a result, business sales and profits grow, fostering a positive investment outlook in the stock market. Additionally, interest rates tend to be low, and monetary policy is supportive, making credit more affordable and accessible, which further encourages investment and stimulates economic growth.
In this phase of the business cycle, economic activity reaches its highest point. Both investment sentiment and consumer confidence are strong. Growth hits its peak, and key economic indicators like GDP and prices remain steady for a time before eventually starting to decline. At this stage, the central bank may consider raising interest rates to manage rising inflationary pressures.
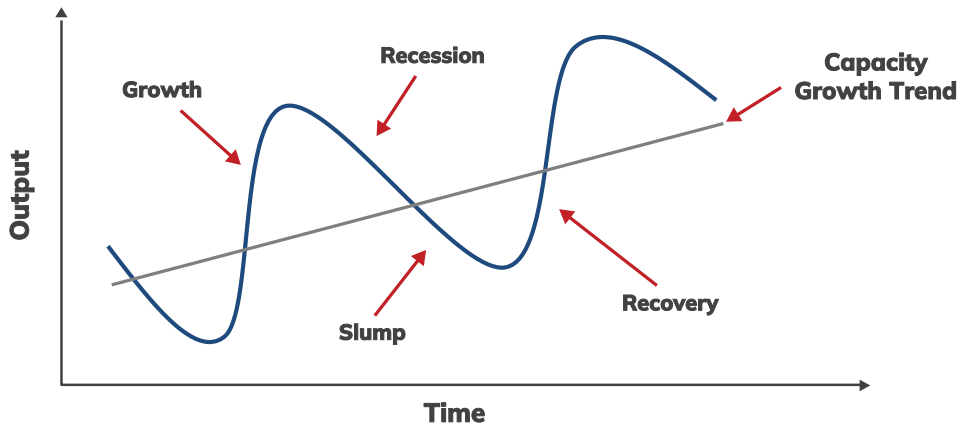
This phase typically signals the onset of a recession, as the economy begins to contract. It's characterized by negative GDP growth, rising unemployment, and a drop in consumer spending. Business profits decline, leading to a more cautious and subdued investment sentiment. During this phase, market volatility often intensifies.
The slum phase marks the bottom of the business cycle and extends from the contraction phase. It represents the lowest level of economic activity, where spending and income remain stagnant at their weakest points.
Here is why it is important for you to understand the business cycle:
Timing of investments
The business cycle helps investors understand the different phases of the economy: expansion, peak, contraction, and slum. Each phase has unique characteristics that can greatly impact investment returns. By recognizing the current phase, you can make better investment decisions. For instance, during an expansion, it may be wise to invest more in stocks, while in a contraction, it could be safer to increase investments in defensive assets like bonds or cash.
Sector rotation
Various sectors perform differently throughout the business cycle. For example, technology and consumer discretionary sectors often do well during expansion, while utilities and consumer staples tend to outperform during contractions. Understanding these patterns allows you to apply a sector rotation strategy, where you adjust your investments to focus on sectors expected to thrive in the current economic phase.
Risk Management
The business cycle offers valuable insights into the broader risk environment. During economic expansion, investors are generally more willing to take on risk, while during contractions, they tend to be more cautious. By aligning your investments with the current stage of the business cycle, you can adjust your risk exposure—reducing potential losses during downturns and seizing opportunities during periods of growth.
Long-Term Planning
Understanding the business cycle encourages a long-term investment approach. Since expansions and contractions occur over extended periods, recognizing these patterns helps you craft strategies that accommodate each phase of the cycle. This way, you can avoid rash decisions based on short-term market changes and stay focused on achieving your long-term goals.
